Bootstrap Modal Options
Intro
Sometimes we really need to make the target on a certain information remaining everything others dimmed behind to make confident we have really gained the targeted visitor's concentration as well as have lots of data wanted to be readily available through the webpage but so huge it absolutely could bore and push the person browsing the web page.
For these circumstances the modal element is pretty much valued. Precisely what it accomplishes is displaying a dialog box having a huge area of the screen diming out whatever other.
The Bootstrap 4 framework has all things needed for developing this kind of feature along with minimum initiatives and a simple user-friendly structure.
Bootstrap Modal Box is streamlined, yet flexible dialog assists powered via JavaScript. They maintain a number of help samples from user notification ending with completely customized material and include a small number of effective subcomponents, sizes, and more.
In what way Bootstrap Modal Form performs
Before beginning by using Bootstrap's modal element, don't forget to read the following because Bootstrap menu decisions have recently replaced.
- Modals are designed with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. They are really placed above everything else within the document and remove scroll from the <body> so that modal content scrolls instead.
- Clicking the modal "backdrop" is going to automatically finalize the modal.
- Bootstrap just provides one modal window at once. Embedded modals aren't supported while we believe them to remain unsatisfactory user experiences.
- Modals usage position:fixed, that can probably sometimes be a bit particular regarding to its rendering. Any time it is possible, put your modal HTML in a high-up position to eliminate probable disturbance coming from other types of components. You'll most likely run into issues while nesting a.modal inside some other fixed component.
- One once more , due to position: fixed, certainly there are a number of warnings with using modals on mobile gadgets.
- In conclusion, the autofocus HTML attribute has absolutely no influence in modals. Here is actually how you have the ability to get the exact same effect together with custom-made JavaScript.
Continue reviewing for demos and usage guidelines.
- As a result of how HTML5 specifies its own semantics, the autofocus HTML attribute provides no effect in Bootstrap modals. To get the exact same result, use certain custom-made JavaScript:
$('#myModal').on('shown.bs.modal', function ()
$('#myInput').focus()
)To start off we need to have a switch on-- an anchor or tab to be clicked on so the modal to get revealed. To perform in this way simply just appoint data-toggle=" modal" attribute followed with determining the modal ID like
data-target="#myModal-ID"
Some example
Now let us develop the Bootstrap Modal Transparent itself-- first we need to get a wrapper component containing the entire aspect-- select it .modal class to it.
A good idea would undoubtedly be at the same time adding the .fade class just to receive smooth emerging transition upon the present of the component.
If those two don't match the trigger won't actually fire the modal up, you would also want to add the same ID which you have defined in the modal trigger since otherwise.
Additionally you might actually desire to incorporate a close button within the header appointing it the class .close plus data-dismiss="modal" attribute but it is not really a condition because if the user hits away in the greyed out component of the screen the modal gets kicked out in any event.
Pretty much this id the system the modal components have in the Bootstrap framework and it pretty much has kept the same in both Bootstrap version 3 and 4. The brand new version comes with a bunch of new methods though it seems that the dev crew believed the modals function well enough the approach they are so they directed their interest off them so far.
Now, lets us take a look at the different kinds of modals and their code.
Modal components
Listed below is a static modal illustration ( representing its position and display have been overridden). Featured are the modal header, modal body ( needed for extra padding), and modal footer ( alternative). We propose that you provide modal headers along with dismiss actions every time possible, or perhaps produce yet another specific dismiss action.
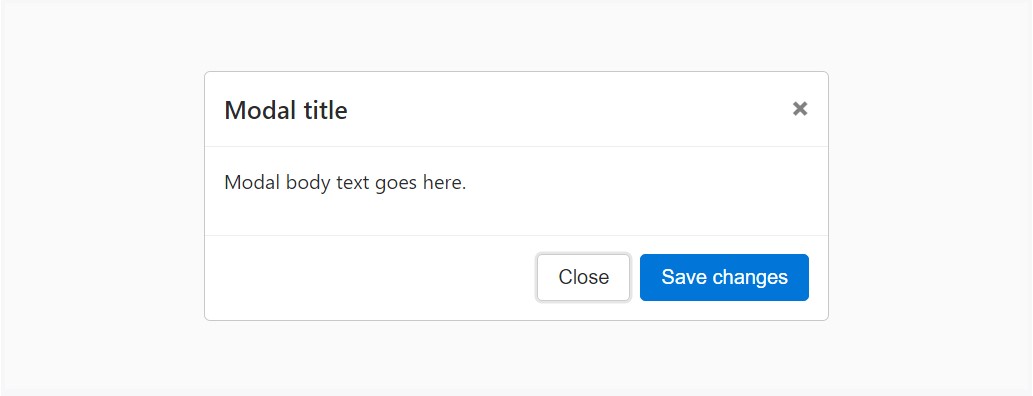
<div class="modal fade">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title">Modal title</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
<p>Modal body text goes here.</p>
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Save changes</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Live demonstration
Whenever you are going to put to use a code shown below - a functioning modal demo is going to be generated as showned on the picture. It will definitely go down and fade in from the high point of the web page.
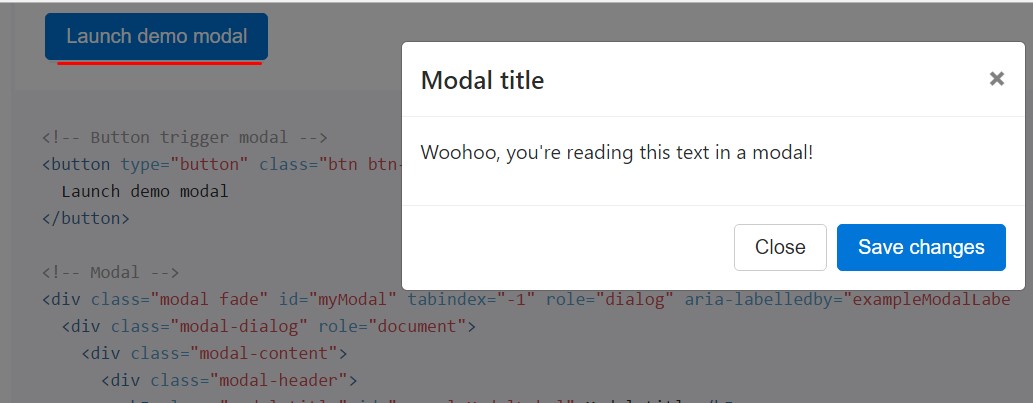
<!-- Button trigger modal -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal">
Launch demo modal
</button>
<!-- Modal -->
<div class="modal fade" id="myModal" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="exampleModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title" id="exampleModalLabel">Modal title</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
...
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Save changes</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Scrolling long web content
The moment modals get extremely long with regard to the user's viewport or tool, they roll independent of the web page itself. Go for the test listed here to notice exactly what we mean.
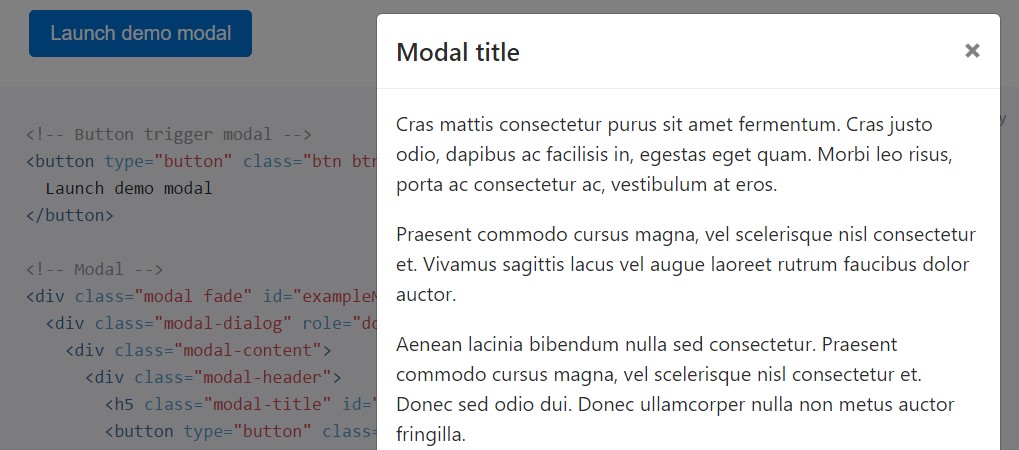
<!-- Button trigger modal -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModalLong">
Launch demo modal
</button>
<!-- Modal -->
<div class="modal fade" id="exampleModalLong" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="exampleModalLongTitle" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title" id="exampleModalLongTitle">Modal title</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
...
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Save changes</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Tooltips and popovers
Tooltips along with popovers might be set within modals as demanded. Any tooltips and popovers within are also automatically dismissed when modals are closed.
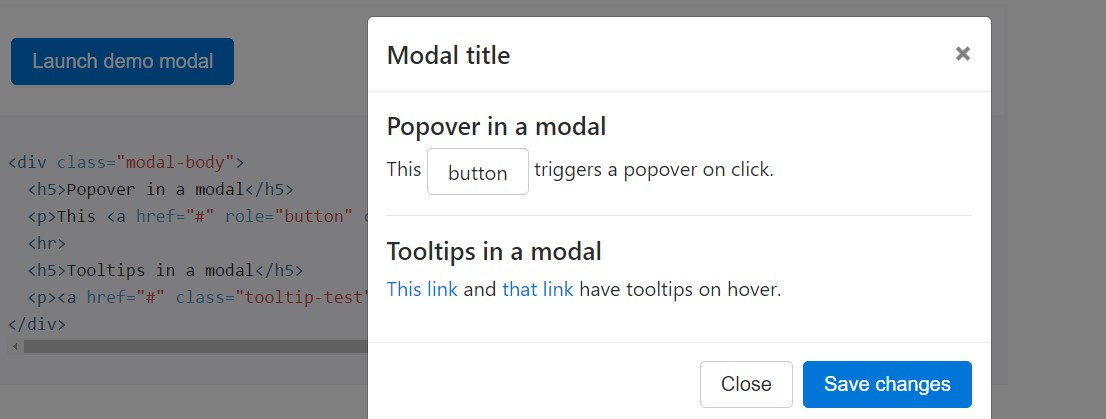
<div class="modal-body">
<h5>Popover in a modal</h5>
<p>This <a href="#" role="button" class="btn btn-secondary popover-test" title="Popover title" data-content="Popover body content is set in this attribute.">button</a> triggers a popover on click.</p>
<hr>
<h5>Tooltips in a modal</h5>
<p><a href="#" class="tooltip-test" title="Tooltip">This link</a> and <a href="#" class="tooltip-test" title="Tooltip">that link</a> have tooltips on hover.</p>
</div>Making use of the grid
Use the Bootstrap grid system within a modal by nesting .container-fluid in the .modal-body. Afterwards, use the normal grid system classes as you would in any place else.
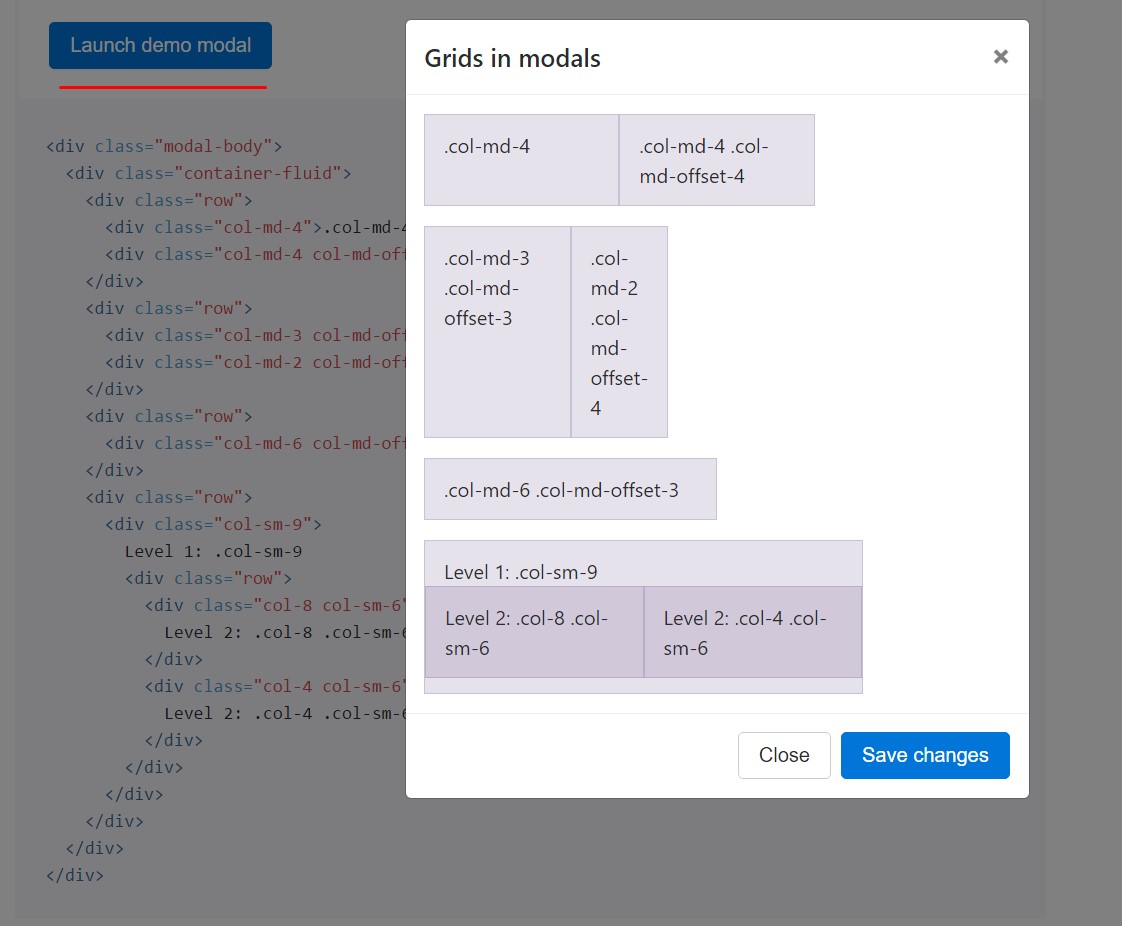
<div class="modal-body">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">.col-md-4</div>
<div class="col-md-4 col-md-offset-4">.col-md-4 .col-md-offset-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-3 col-md-offset-3">.col-md-3 .col-md-offset-3</div>
<div class="col-md-2 col-md-offset-4">.col-md-2 .col-md-offset-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6 col-md-offset-3">.col-md-6 .col-md-offset-3</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-9">
Level 1: .col-sm-9
<div class="row">
<div class="col-8 col-sm-6">
Level 2: .col-8 .col-sm-6
</div>
<div class="col-4 col-sm-6">
Level 2: .col-4 .col-sm-6
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Various modal web content
Feature a group of buttons that all bring on the identical modal having just a little diverse materials? Use event.relatedTarget and HTML data-* attributes ( most likely by using jQuery) to differ the information of the modal according to which button was moused click.
Shown below is a live demo nexted by example HTML and JavaScript. For additional information, looked at the modal events files for specifics on
relatedTarget.
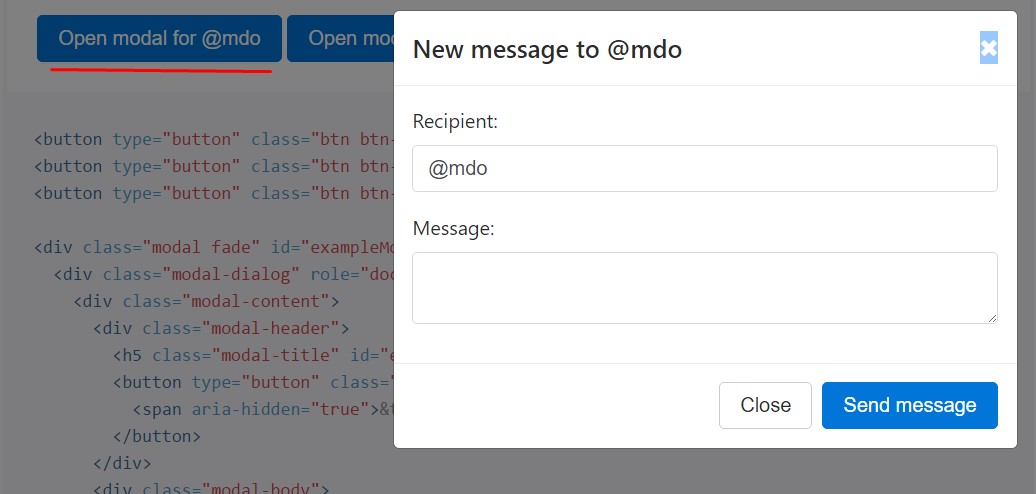
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal" data-whatever="@mdo">Open modal for @mdo</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal" data-whatever="@fat">Open modal for @fat</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal" data-whatever="@getbootstrap">Open modal for @getbootstrap</button>
<div class="modal fade" id="exampleModal" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="exampleModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title" id="exampleModalLabel">New message</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="recipient-name" class="form-control-label">Recipient:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="recipient-name">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="message-text" class="form-control-label">Message:</label>
<textarea class="form-control" id="message-text"></textarea>
</div>
</form>
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Send message</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>$('#exampleModal').on('show.bs.modal', function (event)
var button = $(event.relatedTarget) // Button that triggered the modal
var recipient = button.data('whatever') // Extract info from data-* attributes
// If necessary, you could initiate an AJAX request here (and then do the updating in a callback).
// Update the modal's content. We'll use jQuery here, but you could use a data binding library or other methods instead.
var modal = $(this)
modal.find('.modal-title').text('New message to ' + recipient)
modal.find('.modal-body input').val(recipient)
)Delete animation
For modals that just simply appear instead fade into view, take off the .fade class from your modal markup.
<div class="modal" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="..." aria-hidden="true">
...
</div>Lively heights
In the event that the height of a modal changes while it is open up, you should certainly summon $(' #myModal'). data(' bs.modal'). handleUpdate() to adapt the modal's placement in the event that a scrollbar shows up.
Availability
Implanting YouTube videos clips
Setting YouTube video clips in modals needs added JavaScript not within Bootstrap to instantly stop playback and even more.
Optional sizes
Modals possess two optional proportions, available with modifier classes to be placed on a .modal-dialog. These scales begin at certain breakpoints to evade horizontal scrollbars on narrower viewports.
<!-- Large modal -->
<button class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target=".bd-example-modal-lg">Large modal</button>
<div class="modal fade bd-example-modal-lg" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="myLargeModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog modal-lg">
<div class="modal-content">
...
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Small modal -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target=".bd-example-modal-sm">Small modal</button>
<div class="modal fade bd-example-modal-sm" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="mySmallModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog modal-sm">
<div class="modal-content">
...
</div>
</div>
</div>Application
The modal plugin toggles your hidden content on demand, via data attributes or JavaScript.
Via information attributes
Trigger a modal free from developing JavaScript. Set
data-toggle="modal" on a controller element, like a button, along with a data-target="#foo" or href="#foo" to aim for a particular modal to toggle.
<button type="button" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#myModal">Launch modal</button>Using JavaScript
Call a modal using id myModal using a single line of JavaScript:
$('#myModal'). modal( options).Possibilities
Possibilities may possibly be successfully pass through details attributes or JavaScript. For information attributes, attach the option name to data-, as in data-backdrop="".
Review also the image below:
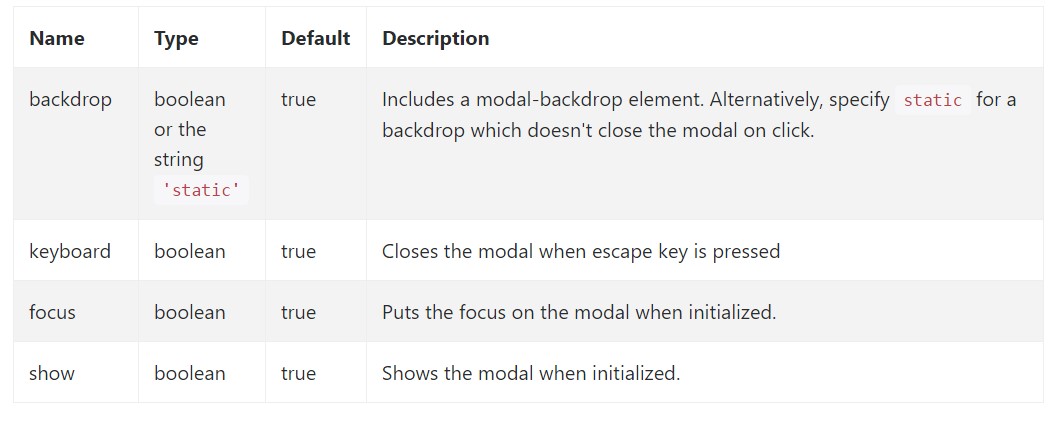
.modal(options)
Activates your information as a modal. Takes an optionally available options object.
$('#myModal').modal(
keyboard: false
).modal('toggle')
Manually button a modal. Go back to the user just before the modal has in fact been demonstrated or hidden (i.e. before the shown.bs.modal or hidden.bs.modal activity happens).
$('#myModal').modal('toggle').modal('show')
Manually opens a modal. Returns to the user right before the modal has really been revealed (i.e. before the shown.bs.modal event happens).
$('#myModal').modal('show').modal('hide')
Manually hides a modal. Come back to the caller right before the modal has in fact been hidden (i.e. just before the hidden.bs.modal event takes place).
$('#myModal').modal('hide')Bootstrap modals events
Bootstrap's modal class exposes a handful of events for entraping in to modal performance. All modal events are fired at the modal itself (i.e. at the <div class="modal">).

$('#myModal').on('hidden.bs.modal', function (e)
// do something...
)Conclusions
We experienced ways in which the modal is established however what exactly could actually be in it?
The response is-- literally whatever-- starting with a extensive heads and conditions plain section with certain headings to the very most complex construction that with the adaptative design techniques of the Bootstrap framework might really be a webpage within the web page-- it is really possible and the choice of applying it falls to you.
Do have in mind however if ever at a certain point the material being soaked the modal gets far too much possibly the much better technique would be positioning the entire subject in a separate webpage for you to have practically more desirable appearance and utilization of the whole screen width provided-- modals a signified for smaller blocks of information prompting for the viewer's treatment .
Take a look at a couple of online video training about Bootstrap modals:
Linked topics:
Bootstrap modals: official documents

W3schools:Bootstrap modal article
Bootstrap 4 with remote modal