Bootstrap Columns Work
Overview
In the last couple years and certainly the next ones to come the whole world of internet spreading more and a lot more extensively across each sort of devices so these days basically half of the views of the web pages online are carried out not really on pc and laptop pc displays however, coming from several mobile gadgets having every kinds of small-sized display measurements. In this degree in the event that a webpage will not present effectively-- indicating to resize and quickly find its own optimal fit on the gadget employed its possibly will get looked away to be changed by a mobile phone friendly webpage offering quite similar service or product.
Aside from that-- the indexing mechanisms like Google make the so called mobile-friendly test and display far down your pages in the search results. This pushing down is even deeper in the case that the search is executed by a mobile phone-- the online search engines consider this specific matter very seriously. In this way not providing a mobile phone friendly page nearly implies not having a webpage in any way.
Steps to work with the Bootstrap Columns Work:
Although what really a web page getting responsive means-- typically-- fitting the entire width of the screen which gets displayed on presenting the features with clear and helpful method at any scale. To deal with this the Bootstrap framework applies so called columns and breakpoints . In a several words the breakpoints are actually predefined screen widths at which a alteration comes about and the Bootstrap Columns jQuery get reordered to hopefully match better. The past edition employed 4 breakpoints and the most modern Bootstrap 4 framework launches one added so they get actually five. Here they are along with the maximum value they stretch to. The exact boundary number itself correlates to the upcoming display size.
Extra small up to 34em ( or 544px) – up to Bootstrap 4 Alpha 5 had the -xs- infix. In Bootstrap 4 alpha 6 this infix is dropped so just the number follows;
Small – from 34em up to 48em ( or 768px ) – has the -sm- infix;
Medium – from 48em up to 62em ( or 992px ) – has the -md- infix;
Large – from 62em up to 75em ( 1200px ) - -lg- infix;
Extra large – 75em and everything above it – the new size in Bootstrap 4 – has the -xl- infix.
Another ideas
The horizontal zone in Bootstrap 4 system becomes divided in 12 parts identical in size-- these are the so called columns-- they all bringing the .col- prefix. Later arrives the display dimension infix which in turn defined down to which screen size the column component will span the defined amount of columns. On the occasion that the display sizing is smaller in size -- the column component takes up the entire display screen width-- as though it was appointed .col-12 (.col-xs-12 up to Bootstrap 4 alpha 5).
Auto style columns
Make use of breakpoint-specific column classes for equal-width columns. Bring in any number of unit-less classes for each breakpoint you require and every Bootstrap Columns Grid will be the equal width.
Equivalent width
For instance, here are two grid formats that used on every gadget and viewport, from xs.

<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 2
</div>
<div class="col">
1 of 2
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
</div>
</div>Putting one column size
Auto-layout for flexbox grid columns also means you can surely put the width of one column and the others are going to automatically resize all around it. You may work with predefined grid classes ( just as revealed below), grid mixins, or possibly inline widths. Take note that the other types of columns will resize despite the width of the center column.

<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-6">
2 of 3 (wider)
</div>
<div class="col">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-5">
2 of 3 (wider)
</div>
<div class="col">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
</div>Variable size content
Utilizing the col- breakpoint -auto classes, columns can size on its own founded on the normal size of its material. This is extremely useful for one line material such as inputs, numbers, and the like. This, coupled with horizontal alignment classes, is really helpful for focusing designs having unequal column sizes as viewport width evolves.
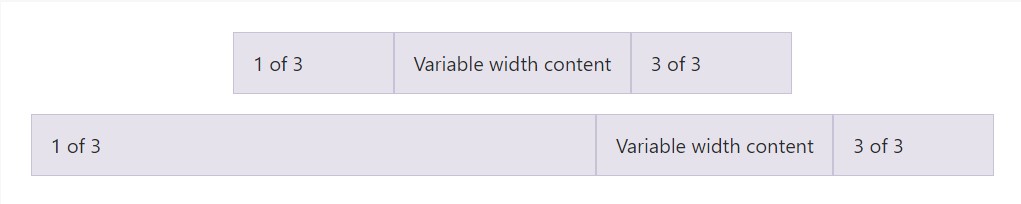
<div class="container">
<div class="row justify-content-md-center">
<div class="col col-lg-2">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-12 col-md-auto">
Variable width content
</div>
<div class="col col-lg-2">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-12 col-md-auto">
Variable width content
</div>
<div class="col col-lg-2">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
</div>Equivalent size multi-row
Build equal-width columns that stretch over multiple rows by fitting a .w-100 just where you want to have the columns to break to a new line. Make the breaks responsive by means of mixing the .w-100 together with some responsive display screen utilities.
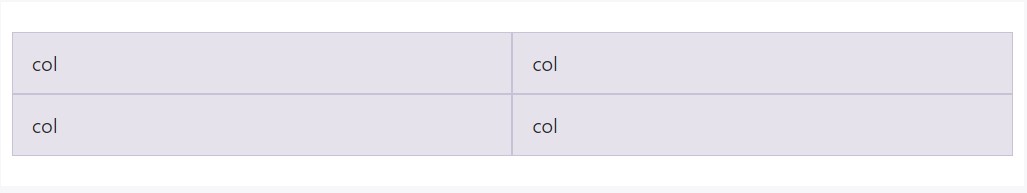
<div class="row">
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="w-100"></div>
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="col">col</div>
</div>One more brand new feature
Another new thing by the most current Alpha 6 build of Bootstrap 4 is assuming that you add in simply just a handful of .col-~ some number here ~ elements spanning less than 12 columns they will actually deliver proportionally to take all of the space readily available on the row and will remain in this way at any display screen width-- even under 32em.
Final thoughts
Well right now you realise the way in which the column features set up the construction as well as responsive activity of the Bootstrap framework and all that is certainly left for you is designing something truly awesome using them.
Take a look at a couple of youtube video short training about Bootstrap columns
Related topics:
Bootstrap columns formal documents

Responsive columns in Bootstrap
Trouble with a heights of the Bootstrap columns